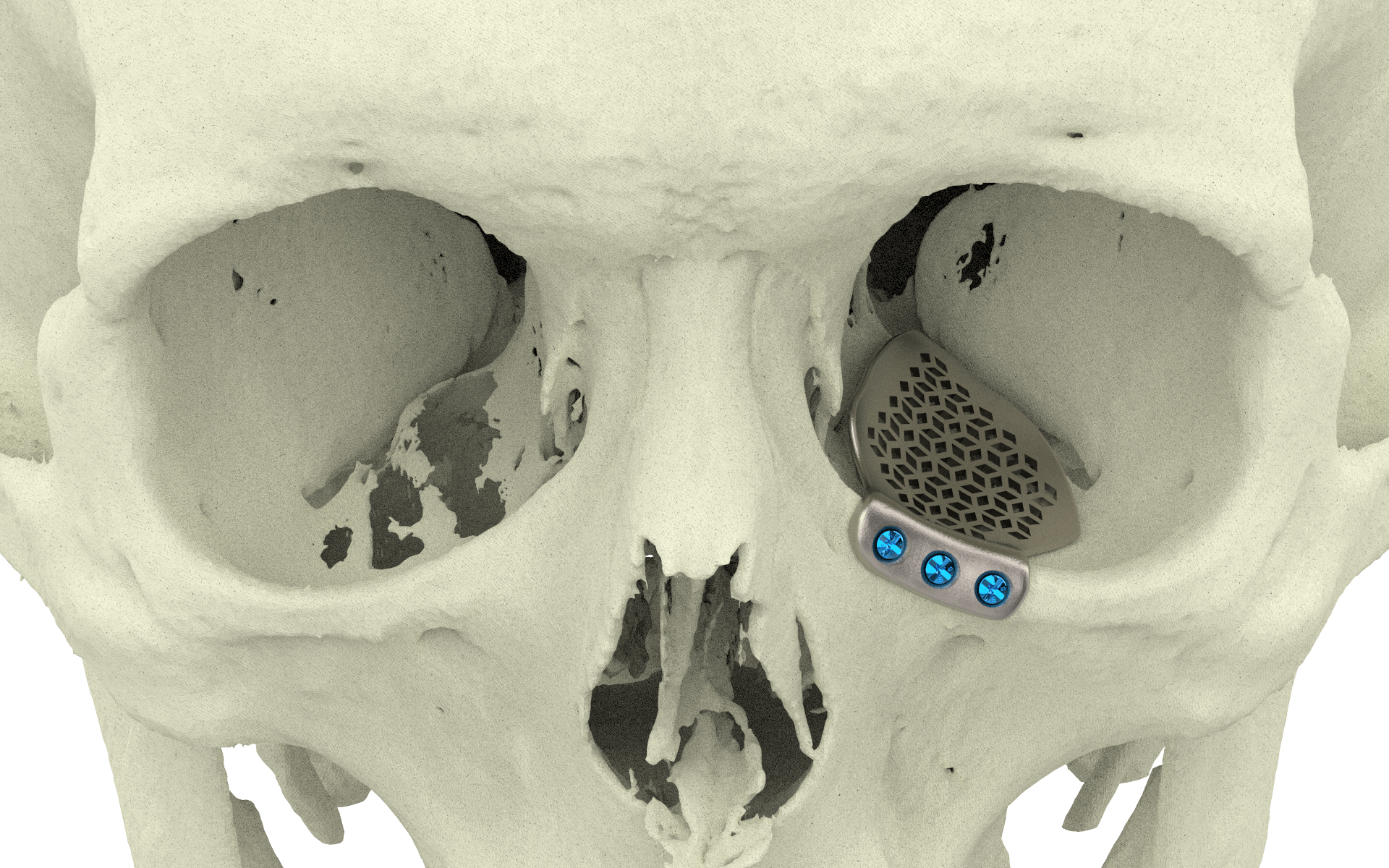
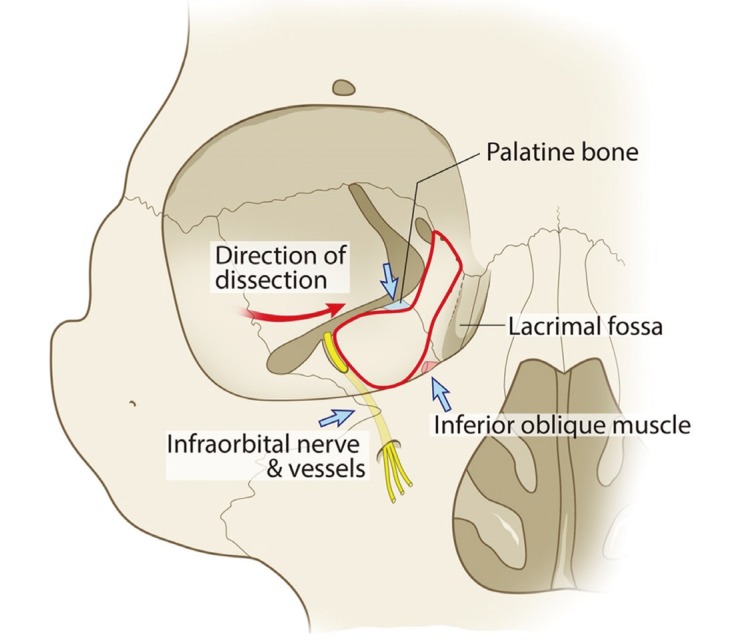
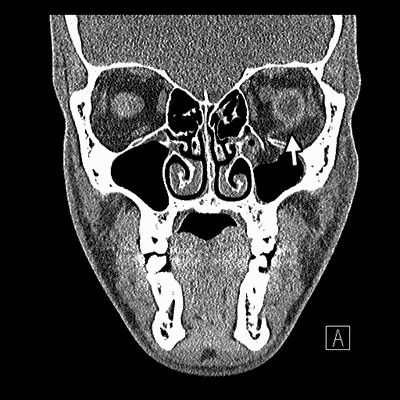
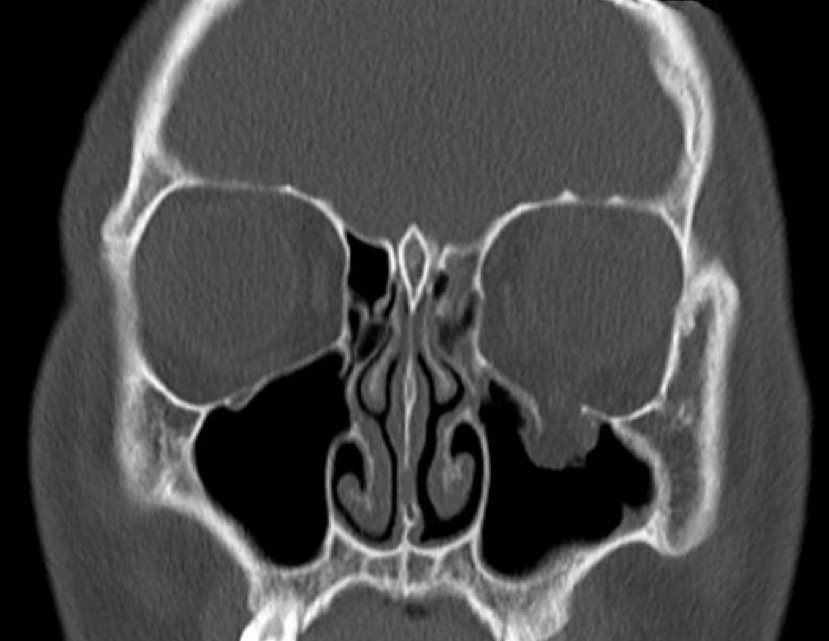
Adult patients who have diplopia or pain on eye movements in the acute setting of an orbital floor fracture should be evaluated again within a week following the injury and if diplopia persists should be seen at weekly intervals as long as the dysmotility is improving.
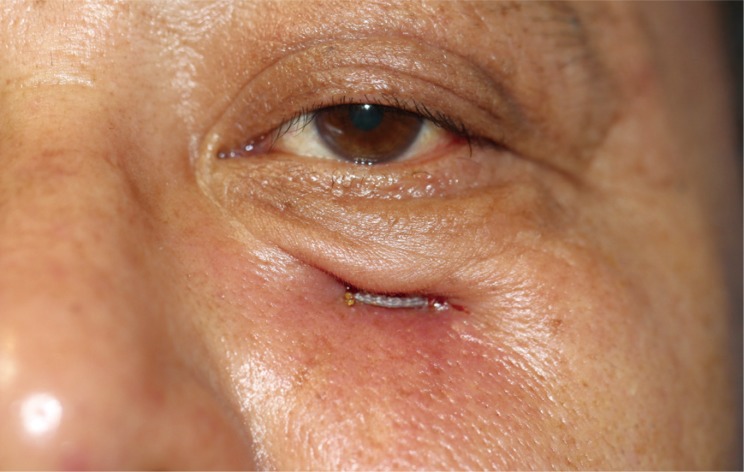
Diplopia after lower orbital floor repair.
Complication the incidence of diplopia after surgical repair of orbital blowout fractures has not been well studied.
A minimum of 6 months follow up was available for all patients included in the study.
Patients who have tenting or deformity of eom on ct scan are more likely to have postoperative diplopia.
An association of preoperative diplopia as well as radiologic evidence of extraocular muscle eom swelling and diplopia 6 months after repair of pure blow out fractures with variousalloplastic.
A minimum of 6 months follow up was available for all patients included in the study.
Ial postoperative complication the incidence of diplopia after surgical repair of orbital blowout fractures has not been well studied.
We retrospectively studied 54 patients who underwent repair of an orbital blowout fracture.
The prognosis of patients was predicted by ct evaluation.
In this retrospective study of 58 patients 36 eyes repaired within 14 days mean of 9 days were compared with 22 eyes repaired at up to 29 days mean of 19 days.
A total of 47 of 54 86.
A total of 47 of 54 86 patients had clinically significant diplopia.
All patients referred during a 2 year period because of persistent diplopia after surgical repair of orbital fracture were categorized according to the degree and pattern of ocular motility.
16 the inferior rectus muscle and the inferior oblique muscle may be involved.
Prognostic ct findings of diplopia after surgical repair of pure orbital blowout fracture pubmed the prognosis of patients was predicted by ct evaluation.
Although diplopia is often an indication for surgery and is presented to patients as a potential postoperative complication the incidence of diplopia after surgical repair of orbital blowout fractures has not been well studied.
A minimum of 6 months follow up was available for all patients included in the study.
Both of them could be weakened by direct trauma 12 17 ischemia so called compartment syndrome 18 and iatrogenic damage during reconstructive surgery 6 13 or restricted by adhesions 19 fibrosis 10 or entrapment under improperly.
We retrospectively studied 54 patients who underwent repair of an orbital blowout fracture.
Diplopia in patients with orbital floor fractures may appear in either up or downgaze or both 9 14 the etiology of this phenomenon has been speculated on since lerman s 1970 study.
We retrospectively studied 54 patients who underwent repair of an orbital blowout fracture.
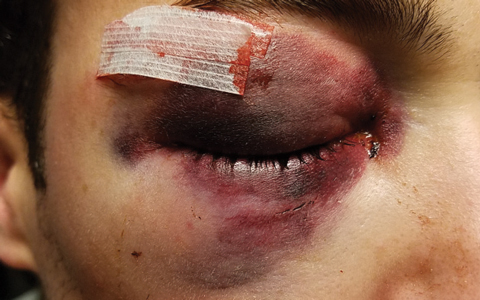
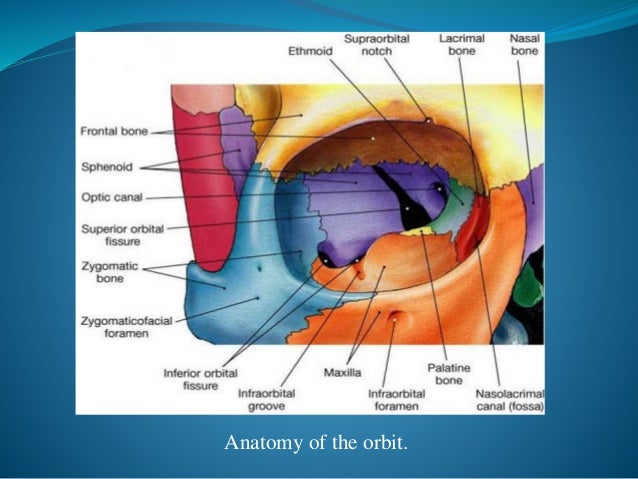


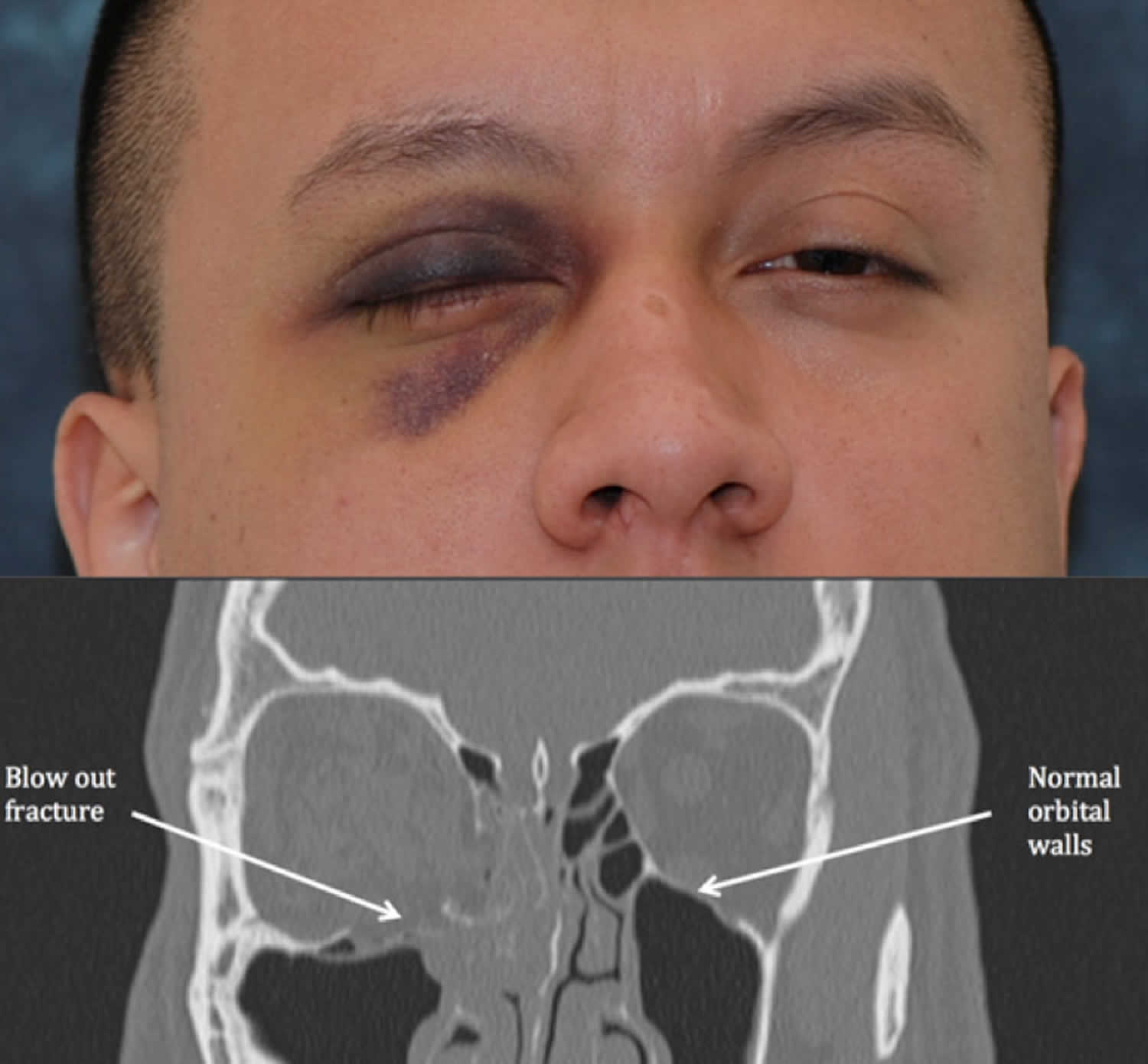
.jpg)